
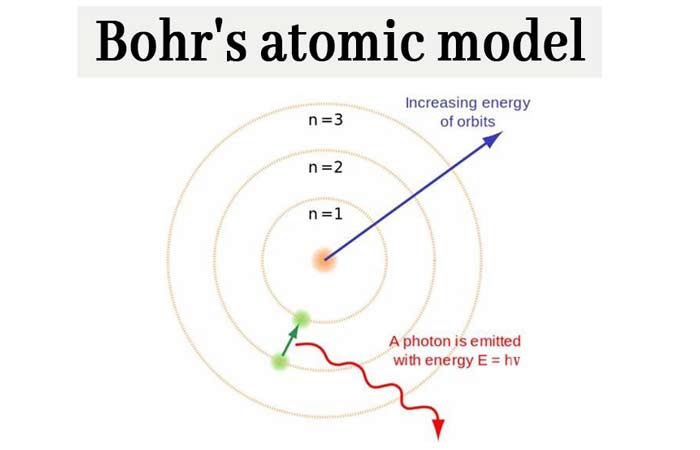
It also explained why the noble gases were inert and why atoms on the left side of the periodic table attract electrons, while those on the right side lose them. According to this model, In an atom, the electrons revolve around the nucleus in definite energy levels called orbits/shells. For example, the shell model explained why atoms got smaller moving across a period (row) of the periodic table, even though they had more protons and electrons. Bohr’s Model is an atomic model proposed by a Danish Physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. The model explained some of the atomic properties of heavier atoms, which had never been reproduced before. Thus, the Bohr model for heavier atoms described electron shells. Once the level was full, additional electrons would be bumped up to the next level. Step 1: find protons, neutrons, and electrons of plutonium atom. It was basically a modified version of Rutherfords Atomic Model wherein Bohr explained that. Currently, it is known that electrons around an atomic nucleus have the properties of matter and wave at the same time, and the position and speed of. Bohr’s Model is an atomic model proposed by a Danish Physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. This model is also called a planetary model because electrons orbiting around an atomic nucleus resemble a planet orbiting the sun. Bohr believed each electron orbit could only hold a set number of electrons. Here’s how you can draw the bohr model of plutonium step by step. Bohrs Atomic Model was introduced by Niels Bohr in 1915. In Bohr’s atomic model, electrons are in a given orbit. More electrons were required to cancel out the positive charge of all of these protons. Heavier atoms contain more protons in the nucleus than the hydrogen atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
